Chemosphere
2012-05-01
The occurrence of synthetic musks in human breast milk in Sichuan, China.
Jie Yin, Hao Wang, Jing Zhang, Naiyuan Zhou, Fudie Gao, Yongning Wu, Jie Xiang, Bing Shao
文献索引:Chemosphere 87(9) , 1018-23, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
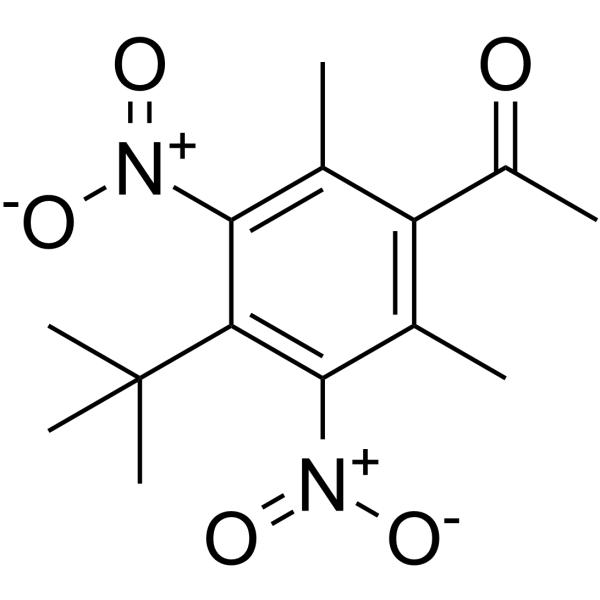
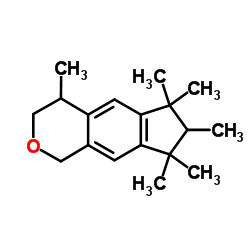
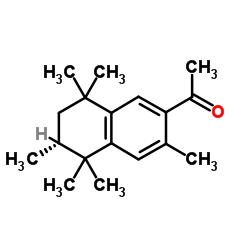
Human breast milk samples collected from mothers (n=110) who lived in Chengdu, Sichuan Province, southwestern China in 2009 were analyzed to determine the concentrations of 13 musk compounds. Possible relationships between musk concentrations and some personal characteristics were also studied. Only five target analytes were detected in the milk samples analyzed, with median concentration values of 16.5, 11.5, 7.85, <1.5 and <1.4ngg(-1)lipid weight for AHTN (7-acetyl-1,1,3,4,4,6-hexamethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene), HHCB (1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-4,6,6,7,8,8-hexamethylcyclopenta[γ]-2-benzopyran), HHCB-lactone (1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-4,6,6,7,8,8-hexamethylcyclopenta[γ]-2-benzopyran-1-one), OTNE ([1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydro-2,3,8,8-tetramethylnaphthalen-2yl]ethan-1-one) and musk ketone (4-tert-butyl-2,6-dimethyl-3,5-dinitroacetophenone, MK), respectively. Mothers who reported high use of hand-cleaning agents, body-cleaning agents, shampoo and hair conditioners, hair dyes and hair gels had significantly elevated milk concentrations of HHCB whereas elevated milk concentrations of AHTN were observed among mothers reporting high use of body-cleaning agents, body lotions, shampoos, hair dyes and hair gels. Younger age showed a significantly positive effect on milk concentrations of both HHCB and AHTN whereas BMI after delivery, the number of children nursed and place of residence (urban or rural) had no significant effect. The estimated median daily intakes of synthetic musks for breast-fed infants were considerably lower than the current provisional tolerable daily intake amounts suggested for adults.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.