| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
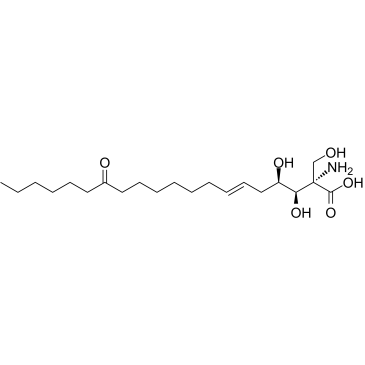 |
嗜热菌杀酵母素
CAS:35891-70-4 |
|
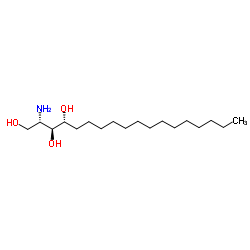 |
糖脂
CAS:554-62-1 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
嗜热菌杀酵母素
CAS:35891-70-4 |
|
 |
糖脂
CAS:554-62-1 |