Electrochemical behavior and voltammetric determination of 2,4,6-triaminopyrimidine at glassy carbon electrode modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes/nafion.
Baocheng Yang, Fei Wang, Sujuan Guo, Baoxian Ye
文献索引:Anal. Sci. 26(10) , 1071-5, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) composite with Nafion was modified on a glass carbon electrode. The modified electrode was then used as a voltammetric sensor in detecting 2,4,6-triaminopyrimidine (TAP). The surface morphology of the Nafion/MWCNTs composite film was characterized by atomic force microscopy (AFM), and the electrochemical behavior of TAP at this sensor was investigated in detail. The results indicated that the Nafion/MWCNTs modified electrode exhibited efficient electrocatalytic oxidation for TAP with relatively high sensitivity, stability and lifetime. Under the optimized condition using linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), the Nafion/MWCNTs modified electrode exhibited a linear voltammetric response for TAP in the concentration range of 2.0 × 10(-7) to 3.6 × 10(-5) mol L(-1), with a detection limit of 5.0 × 10(-8) mol L(-1). The electrode was applied to detect TAP added to human blood serum, with an average recovery value of 101.3%.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
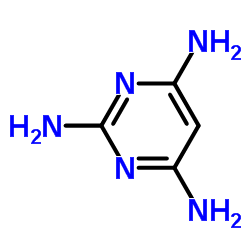 |
2,4,6-三氨基嘧啶
CAS:1004-38-2 |
C4H7N5 |
|
Determination of the driving force for the sodium pump (ENa)...
1987-01-01 [Gen. Pharmacol. 18(6) , 589-92, (1987)] |
|
Mechanism of ammonium transport by intestinal segments follo...
1992-08-01 [J. Urol. 148(2 Pt 1) , 453-7, (1992)] |
|
Factors affecting the potassium concentration at the mucosal...
1990-01-01 [Gut 31(1) , 64-9, (1990)] |
|
Competitive blocking of epithelial sodium channels by organi...
1983-01-01 [J. Membr. Biol. 76(3) , 235-51, (1983)] |
|
Carbon protonation of 2,4,6-triaminopyrimidines: synthesis, ...
2006-06-23 [J. Org. Chem. 71(13) , 4910-8, (2006)] |