Reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction contribute to cirsimaritin-induced apoptosis in human gallbladder carcinoma GBC-SD cells.
Zhiwei Quan, Jun Gu, Ping Dong, Jianhua Lu, Xiangsong Wu, Wenguang Wu, Xiaozhou Fei, Songgang Li, Yong Wang, Jianwei Wang, Yingbin Liu
文献索引:Cancer Lett. 295(2) , 252-9, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In this study, the anticancer effect of cirsimaritin, a natural flavonoid, against human gallbladder carcinoma cell line GBC-SD and the underlying mechanisms were investigated. Cirsimaritin inhibited the growth of tumor cells and induced mitochondrial apoptosis in GBC-SD cells. In addition, cirsimaritin triggered endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and down-regulated the phosphorylation of Akt, while knock-down of CHOP dramatically abrogated the inactivation of Akt and reversed the pro-apoptotic effect of cirsimaritin. Furthermore, cirsimaritin provoked the generation of reactive oxygen species in GBC-SD cells, while the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine almost completely blocked the activation of ER stress and apoptosis, suggesting cirsimaritin-induced reactive oxygen species is an early event that triggers ER stress mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in GBC-SD cells.2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
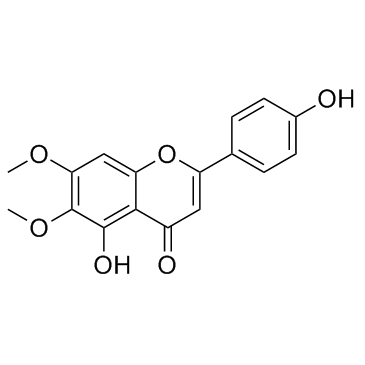 |
蓟黄素
CAS:6601-62-3 |
C17H14O6 |
|
[Studies on flavonoid constituents from herbs of Artemisia o...
2006-12-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 31(23) , 1959-61, (2006)] |
|
[Study on chemical constituents from Incarvillea arguta and ...
2005-09-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30(17) , 1335-8, (2005)] |
|
[Determination of flavonoids in buds of Herba Artemisiae Sco...
2005-04-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30(8) , 591-4, (2005)] |
|
Analysis of vervain flavonoids by HPLC/Diode array detector ...
1999-11-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(11) , 4579-82, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of [methyl-3H]diazepam binding to rat brain membr...
1994-09-01 [Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 15(5) , 385-8, (1994)] |