Topical acetyl salicylate and dipyrone attenuate neurogenic protein extravasation in rat skin in vivo.
M Schmelz, S Weber, M Kress
文献索引:Neurosci. Lett. 290(1) , 57-60, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The effect of topically applied acetyl salicylic acid (ASA) and dipyrone on capsaicin-evoked protein extravasation was investigated by dermal microdialysis in rat. After a baseline of 75 min, capsaicin (1%) was applied epicutaneously under occlusion for 75 min above the capillaries. Topical capsaicin stimulation induced neurogenic protein extravasation with a mean increase of protein concentration in the perfusate of 165+/-27% (mean+/-SEM; n=15), whereas in sham-stimulated sites protein concentration decreased to 73+/-7% of the prestimulation value (n=6). ASA (2-200 mg/ml) and dipyrone (3-300 mg/ml) dose-dependently reduced the capsaicin induced protein extravasation to 118+/-23% (ASA, 200 mg/ml; n=8) and 72+/-9% (dipyrone, 300 mg/ml; n=8) of the prestimulation value. ASA and dipyrone antagonized the excitatory effects of capsaicin on skin nociceptors and thus suppressed the neurogenic protein extravasation.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
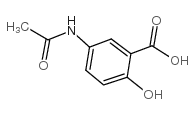 |
5-乙酰氨基水杨酸
CAS:51-59-2 |
C9H9NO4 |
|
Simultaneous determination of 5-aminosalicylic acid, acetyl-...
1995-12-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 14(1-2) , 175-80, (1995)] |
|
Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of balsalazide in ped...
2009-11-01 [J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 49(5) , 571-9, (2009)] |
|
Radical-derived oxidation products of 5-aminosalicylic acid ...
1994-11-04 [J. Chromatogr. B, Biomed. Appl. 661(1) , 57-68, (1994)] |
|
Superoxide inhibition following different stimuli of respira...
1994-01-01 [Dig. Dis. Sci. 39(1) , 145-51, (1994)] |
|
Pharmacokinetic studies of benzalazine.
1994-12-01 [Arzneimittelforschung 44(12) , 1381-3, (1994)] |