Effect of quercetin on the transport of N-acetyl 5-aminosalicylic acid.
Jun Kamishikiryo, Ryusuke Matsumura, Tomohiro Takamori, Narumi Sugihara
文献索引:J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 65(7) , 1037-43, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The aim of this study was to investigate the transporter-mediated transport of N-acetyl 5-aminosalicylic acid (Ac-5-ASA) and the effect of quercetin on Ac-5-ASA transport.Caco-2 cell monolayers grown in Transwells were used to study the transport of Ac-5-ASA in the absence or presence of quercetin, and apical-to-basolateral and basolateral-to-apical apparent permeability (PappAB and PappBA values, respectively) was determined. The effect of transporter inhibitors, such as MK571, quinidine and mitoxantrone, on the transport of Ac-5-ASA was investigated.In the absence of transporter mediators, the transport of Ac-5-ASA was much higher in the basolateral-to-apical direction than in the opposite direction. The PappBA/PappAB ratio of Ac-5-ASA was 4.89. Quercetin inhibited the apical efflux of Ac-5-ASA and decreased the PappBA/PappAB ratio to 1.05. Of the transporter inhibitors, MK571 decreased the PappBA/PappAB ratio to 1.07; however, neither quinidine nor mitoxantrone had an effect on Ac-5-ASA transport.Ac-5-ASA was excreted by multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 from Caco-2 cells, and its transport was inhibited by quercetin. Our findings suggest that dose levels of sulfasalazine or 5-aminosalicylic acid can be decreased by coadministration of quercetin, leading to improved pharmaceutical care for inflammatory bowel diseases.© 2013 Royal Pharmaceutical Society.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
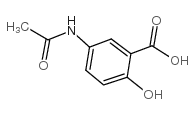 |
5-乙酰氨基水杨酸
CAS:51-59-2 |
C9H9NO4 |
|
Simultaneous determination of 5-aminosalicylic acid, acetyl-...
1995-12-01 [J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 14(1-2) , 175-80, (1995)] |
|
Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of balsalazide in ped...
2009-11-01 [J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 49(5) , 571-9, (2009)] |
|
Radical-derived oxidation products of 5-aminosalicylic acid ...
1994-11-04 [J. Chromatogr. B, Biomed. Appl. 661(1) , 57-68, (1994)] |
|
Superoxide inhibition following different stimuli of respira...
1994-01-01 [Dig. Dis. Sci. 39(1) , 145-51, (1994)] |
|
Pharmacokinetic studies of benzalazine.
1994-12-01 [Arzneimittelforschung 44(12) , 1381-3, (1994)] |