| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
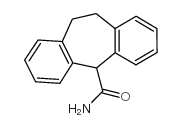 |
环庚米特
CAS:7199-29-3 |
|
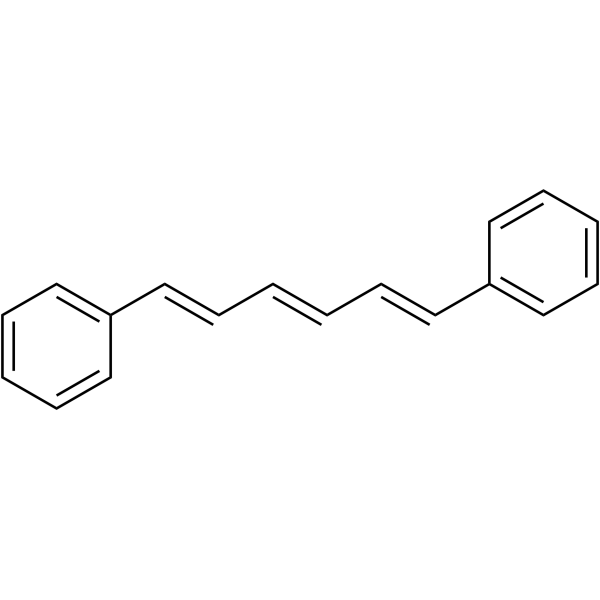 |
1,6-二苯基-1,3,5-己三烯
CAS:1720-32-7 |