Structure of motor nerve terminals in chickens with hereditary muscular dystrophy.
J S Gunther, M S Letinsky
文献索引:Muscle Nerve 8(7) , 568-75, (1985)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The structure and size of 1-week to 1-year-old normal (line 412) and dystrophic (line 413) chicken motor nerve terminals were studied using combined pre- and postsynaptic histologic endplate staining. The main result is that adult dystrophic terminals have abnormal structure and are significantly smaller than normal. These differences occurred progressively during development. At 1 week ex ovo, dystrophic motor nerve terminals were similar to normals in size and appearance. By 8 weeks, differences between normal and dystrophic terminal size and structural organization began to emerge. Qualitatively, beginning at 8 weeks and becoming more frequent by 1 year of age (the endpoint of this study), dystrophic motor endplates differed from normal in having: generally smaller synaptic boutons, often separated by extremely thin branching interconnectives; increasing incidence of multiple innervation; and frequent occurrences of apparent partial or total denervation, terminal sprouting, and reinnervation.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
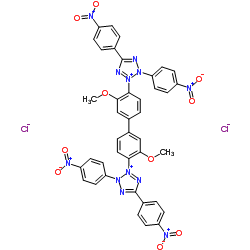 |
四硝基四氮唑蓝(TNBT)
CAS:1184-43-6 |
C40H28Cl2N12O10 |
|
P5-2 of rice black-streaked dwarf virus is a non-structural ...
2015-05-01 [Arch. Virol. 160(5) , 1211-7, (2015)] |
|
Fabrication of mechanically robust, self-cleaning and optica...
2015-08-14 [Nanoscale 7 , 13125-34, (2015)] |
|
Reduced excitability of gp130-deficient nociceptors is assoc...
2014-11-01 [Pflugers Arch. 466(11) , 2153-65, (2014)] |
|
Quantitative aspects of the histochemical tetrazolium salt r...
1985-06-01 [Histochem. J. 17(6) , 707-15, (1985)] |
|
The role of exogenous electron carriers in NAD(P)-dependent ...
1982-01-01 [J. Histochem. Cytochem. 30(1) , 12-20, (1982)] |