| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
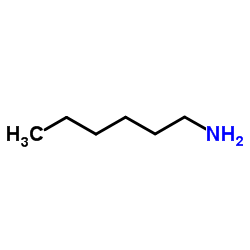 |
正己胺
CAS:111-26-2 |
|
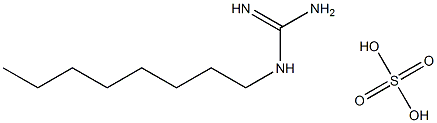 |
1-辛基胍半硫酸盐
CAS:21409-35-8 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
正己胺
CAS:111-26-2 |
|
 |
1-辛基胍半硫酸盐
CAS:21409-35-8 |