| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
聚三氟氯乙烯
CAS:9002-83-9 |
|
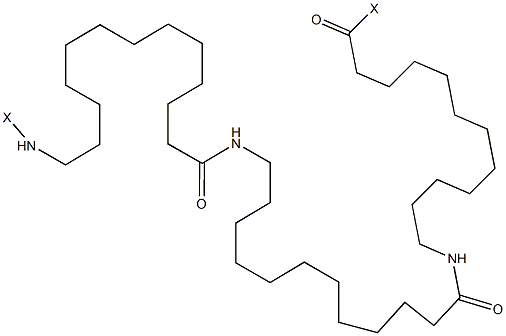 |
尼龙 12
CAS:24937-16-4 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
聚三氟氯乙烯
CAS:9002-83-9 |
|
 |
尼龙 12
CAS:24937-16-4 |