| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
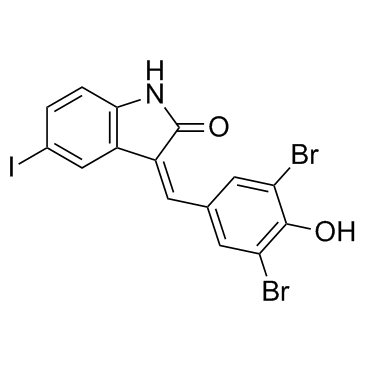 |
GW 5074
CAS:220904-83-6 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
GW 5074
CAS:220904-83-6 |