| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
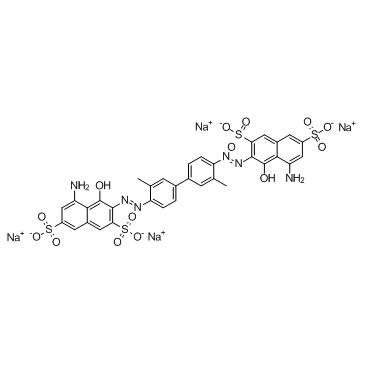 |
直接蓝 14
CAS:72-57-1 |
|
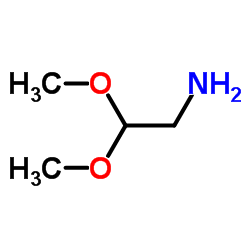 |
氨基乙醛缩二甲醇
CAS:22483-09-6 |
|
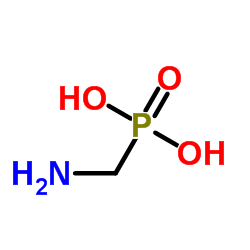 |
氨甲基膦酸
CAS:1066-51-9 |
|
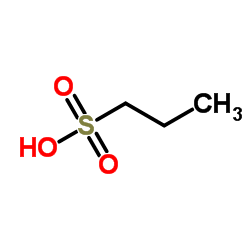 |
1-丙磺酸
CAS:5284-66-2 |
|
 |
8-辛酰氧基芘-1,3,6-三磺酸三钠盐
CAS:115787-84-3 |
|
 |
丙二酰胺
CAS:108-13-4 |