Ether cleaving methyltransferases of the strict anaerobe Acetobacterium dehalogenans: controlling the substrate spectrum by genetic engineering of the N-terminus.
Sandra Kreher, Sandra Studenik, Gabriele Diekert
文献索引:Mol. Microbiol. 78(1) , 230-7, (2010)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The anaerobic cleavage of ether bonds of methoxylated substrates such as vanillate or veratrol in acetogenic bacteria is mediated by multi-component enzyme systems, the O-demethylases. Acetobacterium dehalogenans harbours different inducible O-demethylases with various substrate spectra. Two of these enzyme systems, the vanillate- and the veratrol-O-demethylases, have been characterized so far. One component of this enzyme system, the methyltransferase I (MT I), catalyses the cleavage of the substrate ether bond and the subsequent transfer of the methyl group to a corrinoid protein. For the C-termini of the methyltransferases I of the vanillate- and the veratrol-O-demethylases, a TIM barrel structure of the enzymes was predicted, whereas the N-termini are not part of this conserved structure. The deletion of the N-terminal regions led to a significant increase of activity (up to 20-fold) and an extended substrate spectrum of the mutants, which also comprised non-aromatic compounds such as the thioether methionine and diethylether. The exchange of the N-termini of the two methyltransferases I resulted in chimeric enzymes whose substrate specificities were those of the enzymes from which the N-termini were derived. This demonstrated the crucial role of the N-termini for the substrate specificity of the methyltransferases.© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
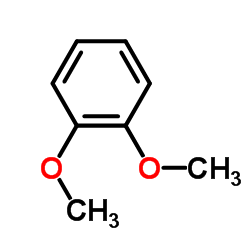 |
1,2-二甲氧基苯
CAS:91-16-7 |
C8H10O2 |
|
Characterization of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Chinese Ric...
2015-07-01 [J. Food Sci. 80 , C1476-89, (2015)] |
|
Kinetic and docking studies of phenol-based inhibitors of ca...
2011-02-15 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 19 , 1381-9, (2011)] |
|
Rotationally resolved electronic spectra of 1,2-dimethoxyben...
2005-10-27 [J. Phys. Chem. A 109(42) , 9456-64, (2005)] |
|
Synthesis and carbonic anhydrase inhibitory properties of no...
2012-02-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22 , 1352-7, (2012)] |
|
X-ray structural characterization of charge delocalization o...
2009-06-04 [Org. Lett. 11(11) , 2253-6, (2009)] |