| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
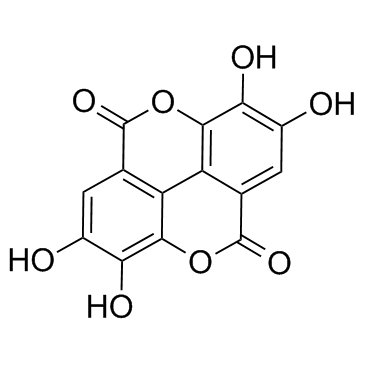 |
鞣花酸
CAS:476-66-4 |
|
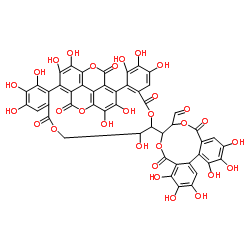 |
安石榴甙; 安石榴苷
CAS:65995-63-3 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
鞣花酸
CAS:476-66-4 |
|
 |
安石榴甙; 安石榴苷
CAS:65995-63-3 |