Biodegradation of a phthalate plasticizer, di-isononyl phthalate (DINP), by Sphingobium chungbukense.
Jae-Min Park, Miri Jeon, Eun-Suk Lim, Hyun-Ju Um, Young-Chang Kim, Jiho Min, Yang-Hoon Kim
文献索引:Curr. Microbiol. 57(5) , 515-8, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
In this study, di-isononyl phthalate (DINP) was efficiently degraded by Sphingobium chungbukense KCTC 2955. The optimal conditions for DINP (100 mg L(-1)) degradation by S. chungbukense in a mineral salts medium were found to be pH 7.0, 30 degrees C, and stirring at 200 rpm. The maximum specific rate of DINP degradation was found to be concentration dependent, with a maximum of 4.12 mg DINP L(-1) h(-1). DINP was transformed rapidly by S. chungbukense, with the formation of monoisononyl phthalate (MIP) and phthalic acid, which subsequently degraded further. These results highlight the potential of this bacterium for removing DINP-contaminated waste in the environment.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
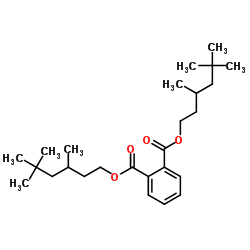 |
邻苯二甲酸二异壬酯
CAS:28553-12-0 |
C26H42O4 |
|
Analysis of phthalates in milk and milk products by liquid c...
2014-10-03 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1362 , 110-8, (2014)] |
|
Monitoring and removal of residual phthalate esters and phar...
2014-07-30 [J. Hazard. Mater. 277 , 53-61, (2014)] |
|
Effects of 4-nonylphenol and/or diisononylphthalate on THP-1...
2012-01-01 [Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 25(2) , 365-76, (2012)] |
|
Consumer product in vitro digestion model: Bioaccessibility ...
2006-03-01 [Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 44(2) , 161-71, (2006)] |
|
Determination of phthalate esters in vegetable oils using di...
2015-08-05 [Anal. Chim. Acta 887 , 237-44, (2015)] |