| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
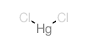 |
氯化汞
CAS:7487-94-7 |
|
 |
藻蓝蛋白
CAS:11016-15-2 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化汞
CAS:7487-94-7 |
|
 |
藻蓝蛋白
CAS:11016-15-2 |