| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
莠去津
CAS:1912-24-9 |
|
 |
谷胱甘肽/5-L-谷氨酰-L-半胱氨酰甘氨酸
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
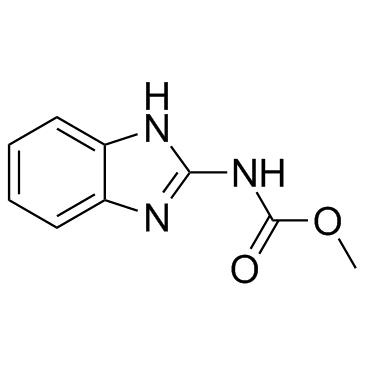 |
多菌灵
CAS:10605-21-7 |