| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
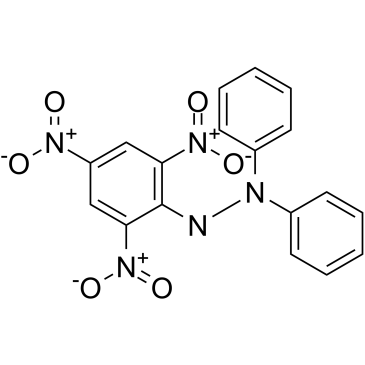 |
2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼基
CAS:1898-66-4 |
|
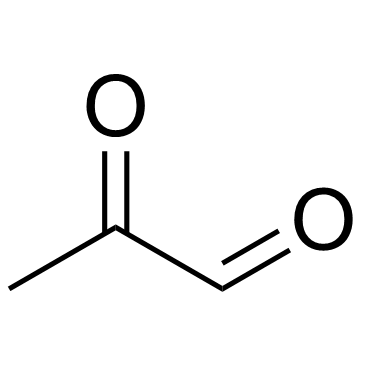 |
丙酮醛
CAS:78-98-8 |
|
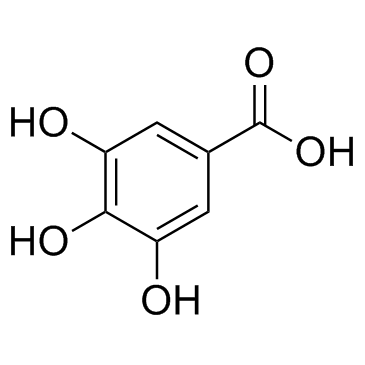 |
没食子酸; 3,4,5-三羟基苯甲酸
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
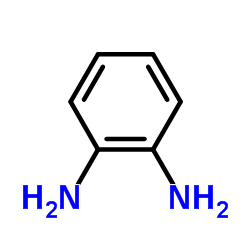 |
邻苯二胺(OPD)
CAS:95-54-5 |
|
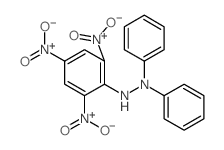 |
1,1-二苯基-2-苦味酰肼
CAS:1707-75-1 |
|
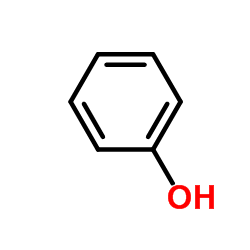 |
苯酚
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
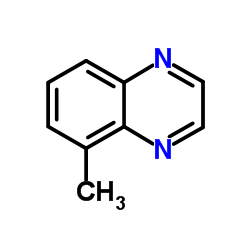 |
5-甲基喹喔啉
CAS:13708-12-8 |
|
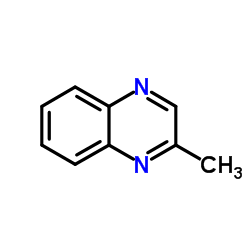 |
2-甲基喹喔啉
CAS:7251-61-8 |