Evaluation of resins for on-bead screening: a study of papain and chymotrypsin specificity using PEGA-bound combinatorial peptide libraries.
S Leon, R Quarrell, G Lowe
文献索引:Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 8(21) , 2997-3002, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
TentaGel, ArgoGel and PEGA resins were evaluated for on-bead biological screening, using a fluorescently-labelled peptide attached to each and assayed for papain activity. Peptide attached to PEGA was cleaved in near quantitative yield at the expected sites, whilst an identical sequence on TentaGel and ArgoGel beads was hydrolysed in very low yields and nonspecifically on ArgoGel. The compatibility of PEGA with enzymes was further demonstrated by the determination of subsite specificities of papain and chymotrypsin using PEGA-bound peptide libraries, which proved to be similar to those observed in free solution.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
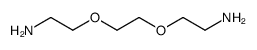 |
聚氧乙烯二胺
CAS:24991-53-5 |
(C2H4O)nC4H12N2O |
|
Synthesis of semitelechelic maleimide poly(PEGA) for protein...
2009-07-13 [Biomacromolecules 10(7) , 1777-81, (2009)] |
|
Construction of highly glycosylated mucin-type glycopeptides...
2006-04-14 [J. Org. Chem. 71(8) , 3051-63, (2006)] |
|
Solid-phase library synthesis, screening, and selection of t...
2002-05-09 [J. Med. Chem. 45(10) , 1971-82, (2002)] |
|
Improved biotransformations on charged PEGA supports.
2003-06-07 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) (11) , 1296-7, (2003)] |
|
Characterization of modified alginate-poly-L-lysine microcap...
1997-09-01 [Artif. Organs 21(9) , 1002-6, (1997)] |