| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
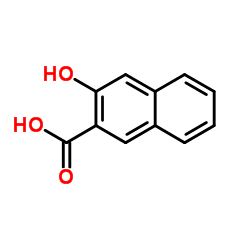 |
2-羟基-3-萘甲酸
CAS:92-70-6 |
|
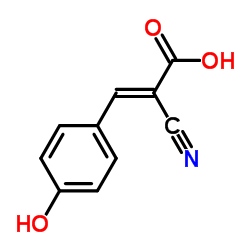 |
α-氰基-4-羟基肉桂酸
CAS:28166-41-8 |