The effectiveness of sodium dichloroisocyanurate treatments against Clostridium difficile spores contaminating stainless steel.
Michael Ungurs, Matthew Wand, Matthew Vassey, Susan O'Brien, Douglas Dixon, Jimmy Walker, J Mark Sutton
文献索引:Am. J. Infect. Control 39(3) , 199-205, (2011)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Clostridium difficile is a major cause of hospital-associated infective diarrhea, and its spore form can persist for months in the hospital environment. Chlorine-based cleaning agents are recommended for eliminating this reservoir of potential infection.To investigate the individual contributions of active chlorine, detergent and mechanical action on decontamination of a C difficile contaminated surface.C difficile spores in test soil were dried onto stainless steel strips and exposed to sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) or NaDCC combined with detergent (NaDCC+) or exposed to these cleaning formulations combined with wiping and/or detergent precleaning. After set contact times, remaining viable spores from the strips were recovered and enumerated by vortexing with glass beads, followed by membrane filtration.Compared with NaDCC, the inclusion of detergent in the NaDCC+ formulation did not improve the effectiveness of decontamination in any exposure-only treatment at concentrations tested (P > .05). Combining wiping with exposure to the cleaning formulations improved decontamination effectiveness with further reductions in spore counts of 1.66- and 2.19-log(10) colony-forming units at 2 and 20 minutes, respectively, using NaDCC, and of 2.46 and 2.56 log(10) colony-forming units at 2 and 20 minutes, respectively, using NaDCC+. Precleaning the strips by wiping with detergent before exposure to NaDCC was more effective than wiping with NaDCC or NaDCC+ at 10 and 20 minutes contact times. Wiping with NaDCC+ was more effective than NaDCC only at a 2-minute contact time. Wiping with detergent followed by subsequent wiping with NaDCC (1,000 ppm) was the most effective treatment tested with a 4.00-log(10) reduction observed.Rigorous precleaning with detergent and the associated physical removal of spores through the mechanical action associated with wiping are important factors in achieving effective decontamination of surfaces when using chlorine-based agents.Copyright © 2011 Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology, Inc. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
二氯异氰尿酸钠
CAS:2893-78-9 |
C3Cl2N3NaO3 | |
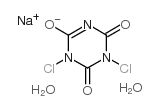 |
二氯异氰尿酸钠 二水合物
CAS:51580-86-0 |
C3H4Cl2N3NaO5 |
|
Assessment of the working range and effect of sodium dichlor...
2012-01-01 [Biofouling 28(1) , 111-20, (2012)] |
|
Effects of pH and oil-in-water emulsions on growth and physi...
2009-01-01 [Int. J. Food Microbiol. 130(2) , 101-7, (2009)] |
|
Analytical method for the quantitative determination of cyan...
2007-06-15 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 853(1-2) , 360-3, (2007)] |
|
Disinfection by-product formation and mitigation strategies ...
2010-07-01 [Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 83(1) , 135-43, (2010)] |
|
Reactive airways dysfunction syndrome from acute inhalation ...
2012-01-01 [Can. Respir. J. 19(3) , e25-8, (2012)] |