| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-半胱氨酸
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
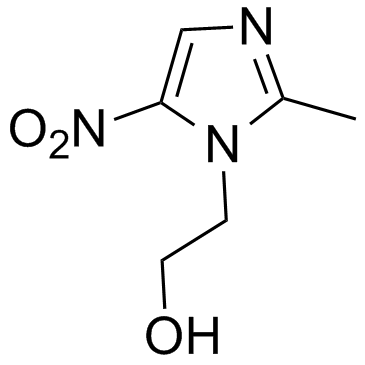 |
甲硝唑
CAS:443-48-1 |
|
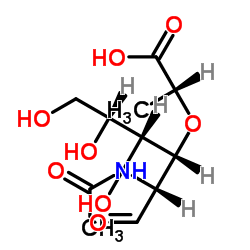 |
N-乙酰胞壁酸
CAS:10597-89-4 |
|
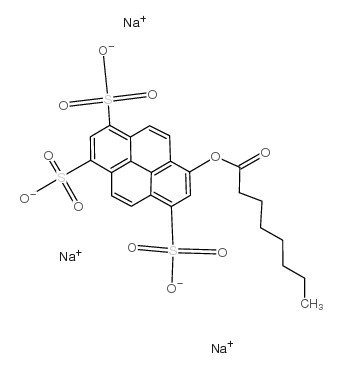 |
8-辛酰氧基芘-1,3,6-三磺酸三钠盐
CAS:115787-84-3 |