| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-半胱氨酸
CAS:52-90-4 |
|
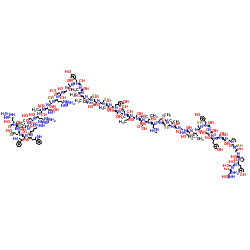 |
表皮生长因子
CAS:62229-50-9 |
|
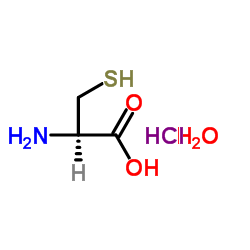 |
L-半胱氨酸盐酸盐,一水合物
CAS:7048-04-6 |
|
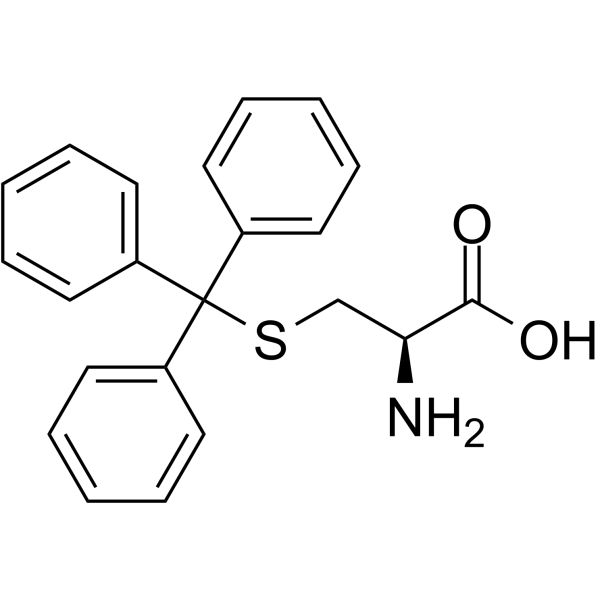 |
S-三苯甲基-L-半胱氨酸
CAS:2799-07-7 |