| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
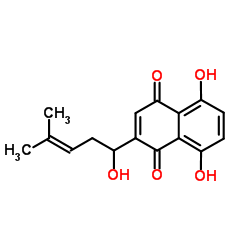 |
莽草素
CAS:54952-43-1 |
|
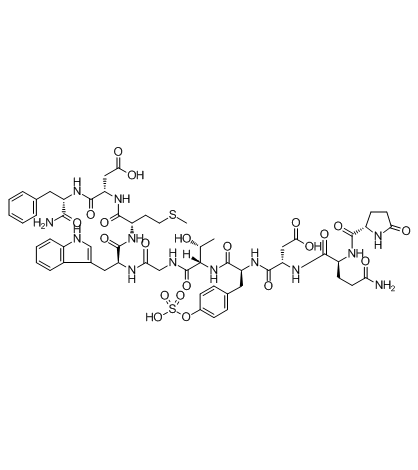 |
雨蛙素
CAS:17650-98-5 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
莽草素
CAS:54952-43-1 |
|
 |
雨蛙素
CAS:17650-98-5 |