Intranasal administration of plasmid DNA-coated nanoparticles results in enhanced immune responses.
Zhengrong Cui, Russell J Mumper
文献索引:J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 54(9) , 1195-203, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Intranasal immunization offers potential forthe elicitation of effective mucosal and systemic immune responses. In this study, a previously reported novel cationic nanoparticle engineered from a microemulsion precursor was further modified, optimized and applied intranasally to mice to explore its potential as a plasmid DNA (pDNA) vaccine delivery system. To this end, more uniform nanoparticles (around 100 nm) containing less cationic surfactant were developed. The pDNA-coated nanoparticles significantly enhanced the specific serum IgG and IgA titres to an expressed model antigen, beta-galactosidase, by 18-28 and 25-30 fold, respectively, when compared with naked pDNA alone. An enhanced splenocyte proliferative response was also observed after immunization with the pDNA-coated nanoparticles. It was concluded that these plasmid DNA-coated nanoparticles may have potential for immunization via the nasal route.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
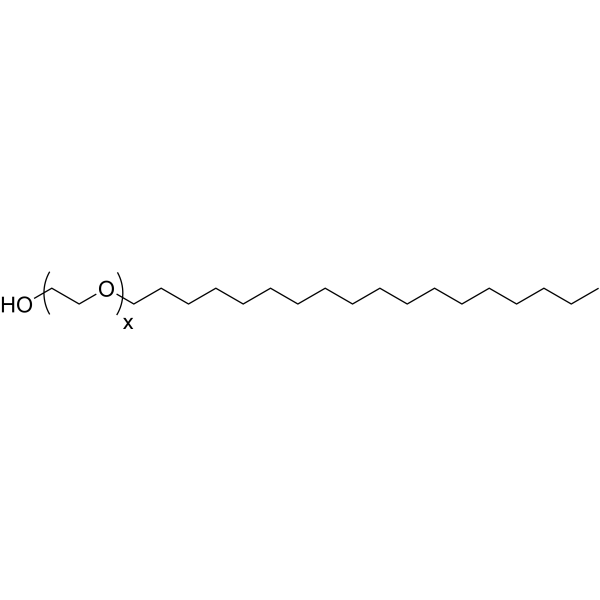 |
S100聚氧乙烯硬脂酸酯
CAS:9005-00-9 |
(C2H4O)nC18H38O |
|
Tailored microcrystal growth: a facile solution-phase synthe...
2011-10-11 [Adv. Mater. 23(38) , 4431-4, (2011)] |
|
Inhibitory effects of polyoxyethylene stearate, PANTA, and n...
1997-11-01 [J. Clin. Microbiol. 35(11) , 2791-4, (1997)] |
|
A collaborative evaluation of the cytotoxicity of two surfac...
2003-02-01 [J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 19(1) , 11-21, (2003)] |
|
Tresyl-based conjugation of protein antigen to lipid nanopar...
2010-01-01 [Int. J. Pharm. 401(1-2) , 87-92, (2010)] |
|
Templating multiple length scales by combining phase separat...
2008-12-15 [J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 328(2) , 374-84, (2008)] |