Persistence of external chloride and DIDS binding after chemical modification of Glu-681 in human band 3.
S Bahar, C T Gunter, C Wu, S D Kennedy, P A Knauf
文献索引:Am. J. Physiol. 277(4 Pt 1) , C791-9, (1999)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Although its primary function is monovalent anion exchange, the band 3 protein also cotransports divalent anions together with protons at low pH. The putative proton binding site, Glu-681 in human erythrocyte band 3, is conserved throughout the anion exchanger family (AE family). To determine whether or not the monovalent anion binding site is located near Glu-681, we modified this residue with Woodward's reagent K (N-ethyl-5-phenylisoxazolium-3'-sulfonate; WRK). Measurements of Cl(-) binding by (35)Cl-NMR show that external Cl(-) binds to band 3 even when Cl(-) transport is inhibited approximately 95% by WRK modification of Glu-681. This indicates that the external Cl(-) binding site is not located near Glu-681 and thus presumably is distant from the proton binding site. DIDS inhibits Cl(-) binding even when WRK is bound to Glu-681, indicating that the DIDS binding site is also distant from Glu-681. Our data suggest that the DIDS site and probably also the externally facing Cl(-) transport site are located nearer to the external surface of the membrane than Glu-681.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
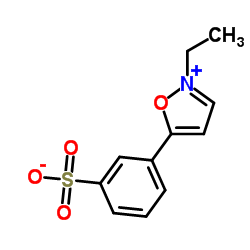 |
2-乙基-5-苯基异恶唑-3'-磺酸盐
CAS:4156-16-5 |
C11H11NO4S |
|
[Synthesis of electroconductive polyaniline using immobilize...
2009-01-01 [Prikl. Biokhim. Mikrobiol. 45(1) , 33-7, (2009)] |
|
The carboxyl side chain of glutamate 681 interacts with a ch...
2003-02-18 [Biochemistry 42(6) , 1589-602, (2003)] |
|
Effect of protein-modifying reagents on ecto-apyrase from ra...
2000-01-01 [Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 32(1) , 105-13, (2000)] |
|
Woodward's reagent K inactivation of Escherichia coli L-thre...
1996-02-01 [Protein Sci. 5(2) , 382-90, (1996)] |
|
Acidic residue modifications restore chaperone activity of β...
2011-11-01 [Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 49(4) , 616-21, (2011)] |