| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
利培酮
CAS:106266-06-2 |
|
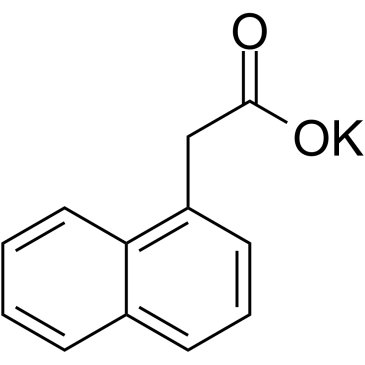 |
1-萘乙酸钾
CAS:15165-79-4 |
|
 |
氯安定
CAS:1622-61-3 |
|
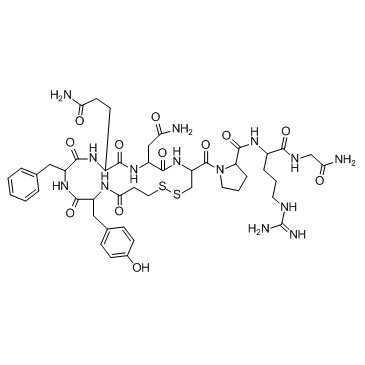 |
去氨加压素
CAS:16679-58-6 |
|
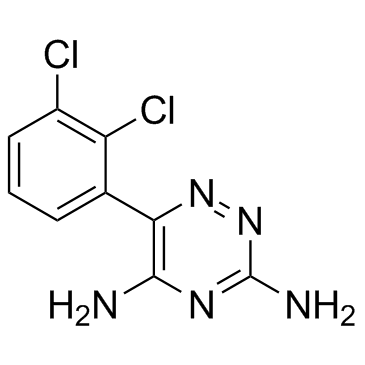 |
拉莫三嗪
CAS:84057-84-1 |
|
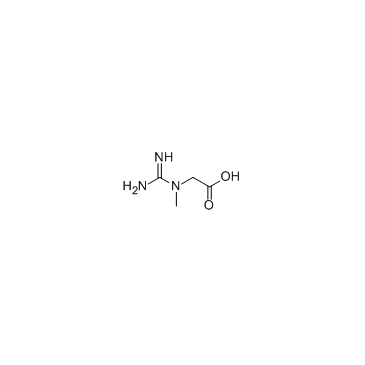 |
肌酸
CAS:57-00-1 |