Adding l-lysine derivatives to the genetic code of mammalian cells with engineered pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetases.
Takahito Mukai, Takatsugu Kobayashi, Nobumasa Hino, Tatsuo Yanagisawa, Kensaku Sakamoto, Shigeyuki Yokoyama
文献索引:Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 371(4) , 818-22, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We report a method for site-specifically incorporating l-lysine derivatives into proteins in mammalian cells, based on the expression of the pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase (PylRS)-tRNA(Pyl) pair from Methanosarcina mazei. Different types of external promoters were tested for the expression of tRNA(Pyl) in Chinese hamster ovary cells. When tRNA(Pyl) was expressed from a gene cluster under the control of the U6 promoter, the wild-type PylRS-tRNA(Pyl) pair facilitated the most efficient incorporation of a pyrrolysine analog, N(epsilon)-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-l-lysine (Boc-lysine), into proteins at the amber position. This PylRS-tRNA(Pyl) system yielded the Boc-lysine-containing protein in an amount accounting for 1% of the total protein in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells. We also created a PylRS variant specific to N(epsilon)-benzyloxycarbonyl-l-lysine, to incorporate this long, bulky, non-natural lysine derivative into proteins in HEK293. The recently reported variant specific to N(epsilon)-acetyllysine was also expressed, resulting in the genetic encoding of this naturally-occurring lysine modification in mammalian cells.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
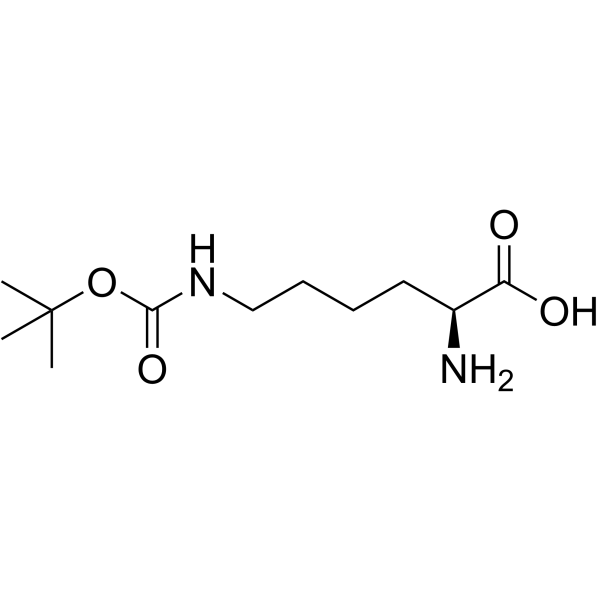 |
N(e)-Boc-L-赖氨酸
CAS:2418-95-3 |
C11H22N2O4 |
|
Evidence that malondialdehyde-derived aminoenimine is not a ...
2001-05-01 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 14(5) , 473-5, (2001)] |
|
Nanoassembly of surfactants with interfacial drug-interactiv...
2013-01-07 [Mol. Pharm. 10(1) , 187-98, (2013)] |
|
Formation of glyoxal, methylglyoxal and 3-deoxyglucosone in ...
1999-11-15 [Biochem. J. 344 Pt 1 , 109-16, (1999)] |
|
Chain-length dependence for secondary structure formation of...
1984-01-01 [Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 23(1) , 47-54, (1984)] |
|
Well-defined homopolypeptides, copolypeptides, and hybrids o...
2011-06-13 [Biomacromolecules 12 , 2396-2406, (2011)] |