Insights into the origin of high activity and stability of catalysts derived from bulky, electron-rich monophosphinobiaryl ligands in the Pd-catalyzed C-N bond formation.
Eric R Strieter, Donna G Blackmond, Stephen L Buchwald
文献索引:J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125(46) , 13978-80, (2003)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
A comparative kinetic examination of catalyst systems based on several monophosphinobiaryl ligands is reported. The bulk of the phosphine ligand controls the catalytic activity and the rate of catalyst activation with the catalyst based on 2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2',4',6'-triisopropylbiphenyl providing the greatest activity and fastest activation. In the case where catalyst activation is slow (i.e., use of the smaller ligands such as 2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2'-methylbiphenyl in combination with Pd(OAc)2) stirring the amine with the catalyst/base mixture prior to the commencement of the reaction increases the reaction rate along with the rate of catalyst activation. Kinetic isotope effects established that the catalyst activation process occurs through a beta-hydride elimination pathway.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
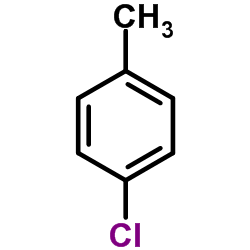 |
对氯甲苯
CAS:106-43-4 |
C7H7Cl |
|
QSPR modeling of octanol/water partition coefficient for vit...
2008-04-01 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43 , 714-40, (2008)] |
|
Optimizations of packed sorbent and inlet temperature for la...
2014-08-22 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 221-9, (2014)] |
|
Mechanism-Based Post-Translational Modification and Inactiva...
2015-11-20 [ACS Chem. Biol. 10 , 2501-11, (2015)] |
|
Effects of p-chlorotoluene (PCT) on rat lung and liver benzo...
1997-02-07 [J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 50(2) , 159-72, (1997)] |
|
Molecular structure and vibrational spectra of o-chlorotolue...
2011-03-01 [Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 78(3) , 1126-32, (2011)] |