| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
β-雌二醇3,17-二硫酸二钾盐
CAS:17046-60-5 |
|
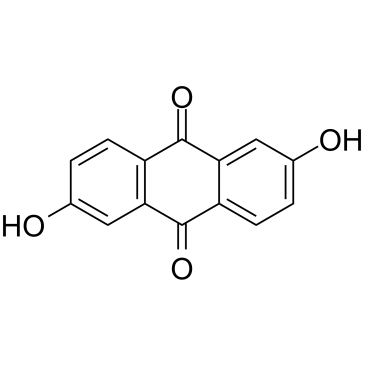 |
2,6-二羟基蒽醌
CAS:84-60-6 |