Mass spectral analysis of some derivatives and in vitro metabolites of steviol, the aglycone of the natural sweeteners, stevioside, rebaudioside A, and rubusoside.
C M Compadre, R A Hussain, N P Nanayakkara, J M Pezzuto, A D Kinghorn
文献索引:Biomed. Environ. Mass Spectrom. 15(4) , 211-22, (1988)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Steviol (ent-13-hydroxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid), the aglycone of various plant-derived glycoside sweeteners consumed by human populations, is known to be mutagenic toward Salmonella tymphimurium strain TM677 when metabolically activated using a 9000 x g supernatant fraction derived from the liver of Aroclor 1254-pretreated rats. Mass spectral analysis of this diterpenoid and some analogs revealed characteristic patterns reflecting differential stereochemistry at the C/D rings and variations in the nature of the substituents present. Such information has been used to help identify several in vitro metabolites of steviol in conditions known to produce a mutagenic response, when analyzed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. The major pathways of such steviol mammalian metabolism proved to be allylic oxidation and epoxidation. 15-Oxosteviol, a product of oxidation of the major steviol metabolite, 15alpha-hydroxysteviol, was found to be a direct-acting mutagen [corrected].
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
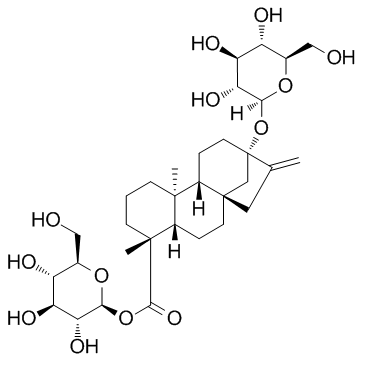 |
甜茶苷
CAS:64849-39-4 |
C32H50O13 |
|
Cytotoxic and antiangiogenic paclitaxel solubilized and perm...
2015-02-01 [Anticancer Drugs 26(2) , 167-79, (2014)] |
|
[Identification and biotransformation properties of a bacter...
2011-01-01 [Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 51(1) , 43-9, (2011)] |
|
[Study on quality control of Rubus suavissimus].
2008-11-01 [Zhong Yao Cai 31(11) , 1734-7, (2008)] |
|
Further study on the 1,4-alpha-transglucosylation of rubusos...
1991-02-01 [Agric. Biol. Chem. 55(2) , 449-53, (1991)] |
|
Quantitative and fingerprint analyses of Chinese sweet tea p...
2009-02-11 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(3) , 1076-83, (2009)] |