Combined use of nonculture-based lab techniques in the diagnosis and management of critically ill patients with invasive fungal infections.
Javier Pemán, Rafael Zaragoza
文献索引:Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 10(11) , 1321-30, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Invasive fungal infections are associated with high morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients due, in part, to diagnostic difficulties in the early stages. Nonculture-based techniques such as (1,3)-β-d-glucan, galactomannan, mannan and antimannan antibodies, Candida albicans germ tube-specific antibodies or fungal DNA are required for earlier diagnosis, prognostic information and monitoring outcome. A decision-tree algorithm based on the combination of nonculture-based techniques is suggested to optimize the diagnosis and evolution of critically ill patients at risk of invasive mycoses. The use of (1,3)-β-d-glucan and blood cultures twice a week is proposed; if positive, treatment initiation is recommended alongside the performance of the nonculture-based microbiological tool depending on suspected mycoses and the availability of techniques.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
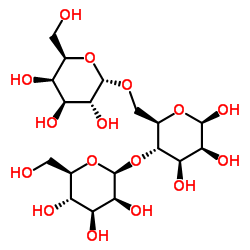 |
瓜尔豆胶酶解物
CAS:11078-30-1 |
C18H32O16 |
|
Hydrolyzed galactomannan-modified nanoparticles and flower-l...
2013-06-01 [J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 9(6) , 1076-87, (2013)] |
|
Invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematological malign...
2013-02-01 [Int. J. Infect. Dis. 17(2) , e101-9, (2013)] |
|
Variables affecting the performance of galactomannan assay i...
2013-01-01 [Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 31(1) , 34-9, (2013)] |
|
False positive galactomannan test after ice-pop ingestion.
2013-07-04 [N. Engl. J. Med. 369(1) , 97-8, (2013)] |
|
The interaction between piperacillin-tazobactam and Aspergil...
2013-02-01 [Infection 41(1) , 293-4, (2013)] |