| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
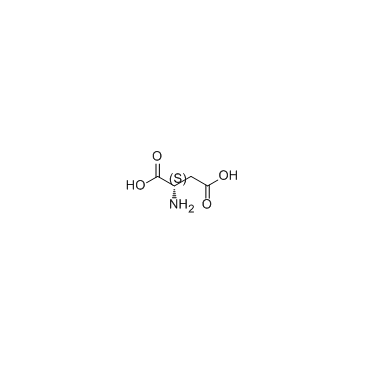 |
L-天门冬氨酸
CAS:56-84-8 |
|
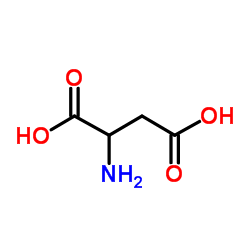 |
DL-天门冬氨酸
CAS:617-45-8 |
|
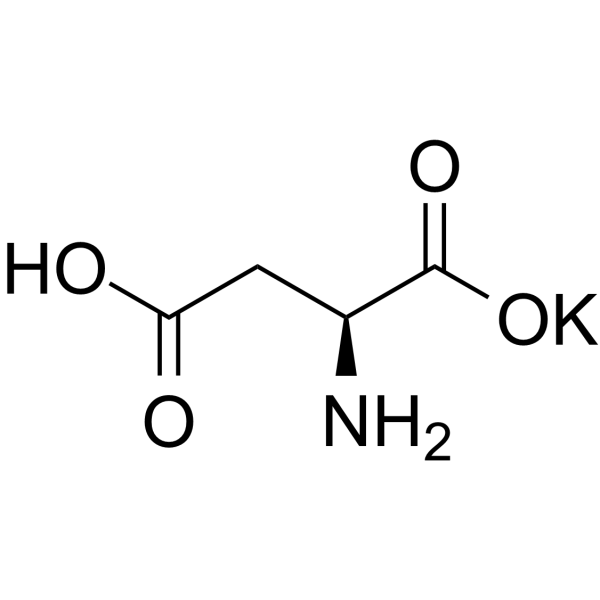 |
L-天冬氨酸钾
CAS:1115-63-5 |
|
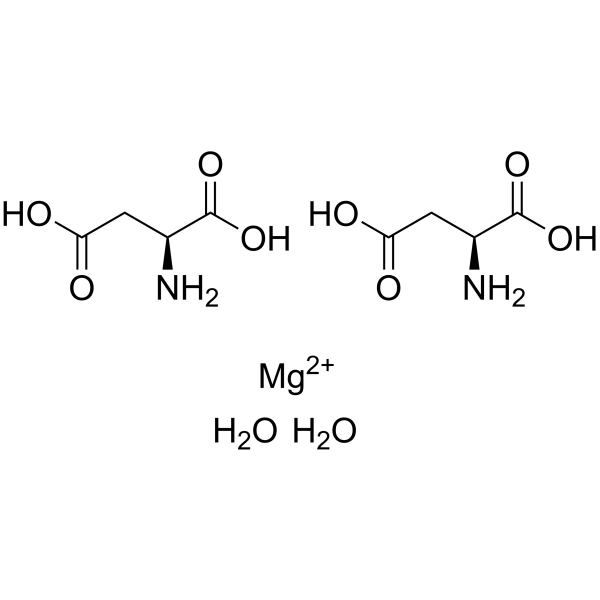 |
L-天冬氨酸 半镁盐 二水合物
CAS:215533-00-9 |