Effect of spores of saprophytic fungi on phytoalexin accumulation in seeds of frog-eye leaf spot and stem canker-resistant and -susceptible soybean (Glycine max L.) cultivars.
W S Garcez, D Martins, F R Garcez, M R Marques, A A Pereira, L A Oliveira, J N Rondon, A D Peruca
文献索引:J. Agric. Food Chem. 48(8) , 3662-5, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Two saprophytic fungi (Mucor ramosissimus and Rhizopus sp.) were tested for their ability to induce phytoalexin production by seeds of frog-eye leaf spot and stem canker-resistant and -susceptible soybean (Glycine max L.) cultivars. Only M. ramosissimus was shown to elicit a response and qualitative differences in phytoalexin accumulation were found between the susceptible and resistant cultivars. Glyceollins I, II, and III and glycinol were isolated from the susceptible cultivar, whereas Glyceollins I, II, and III, glycinol, glyceocarpin, genistein, isoformononetin, and N-acetyltyramine accumulated in the resistant cultivar in response to the same fungal elicitor. Genistein was found to be an inducibly formed isoflavonoid instead of a constitutive metabolite in the resistant cultivar, whereas N-acetyltyramine is described for the first time as a soybean phytoalexin. All the compounds, except genistein, showed fungitoxic activity against Cladosporium sphaerospermum. Spectral data of the pterocarpan phytoalexins, genistein, and N-acetyltyramine are also given in this work.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
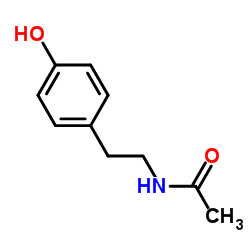 |
N-(4-羟基苯基)乙酰胺
CAS:1202-66-0 |
C10H13NO2 |
|
Selective nanomolar detection of dopamine using a boron-dope...
2009-05-15 [Anal. Chem. 81(10) , 4089-98, (2009)] |
|
Mechanistic and structural analysis of Drosophila melanogast...
2014-12-16 [Biochemistry 53(49) , 7777-93, (2014)] |
|
Effect of acetyl derivatives of some sympathomimetic amines ...
1977-02-01 [Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 40(2) , 247-58, (1977)] |
|
Partial purification and properties of N-acetylhistamine dea...
1976-07-08 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 438(2) , 532-9, (1976)] |
|
Changes in the content of brain biogenic amine associated wi...
2012-01-01 [PLoS ONE 7(8) , e43377, (2012)] |