| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
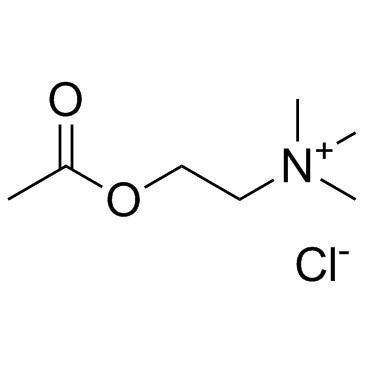 |
氯化乙酰胆碱; 乙酰氯化胆碱
CAS:60-31-1 |
|
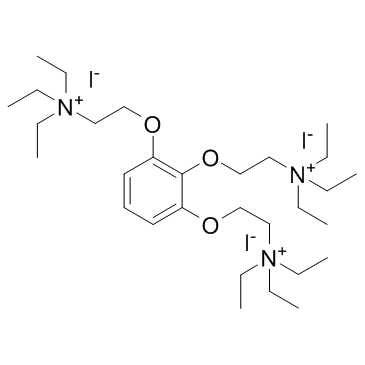 |
加拉碘铵
CAS:65-29-2 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化乙酰胆碱; 乙酰氯化胆碱
CAS:60-31-1 |
|
 |
加拉碘铵
CAS:65-29-2 |