| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
丙泊酚
CAS:2078-54-8 |
|
 |
盐酸氯氨酮
CAS:1867-66-9 |
|
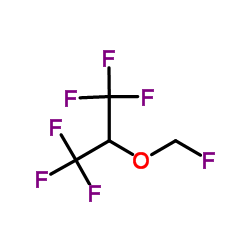 |
氟甲基-1,1,1,3,3,3-六氟异丙基醚
CAS:28523-86-6 |