| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
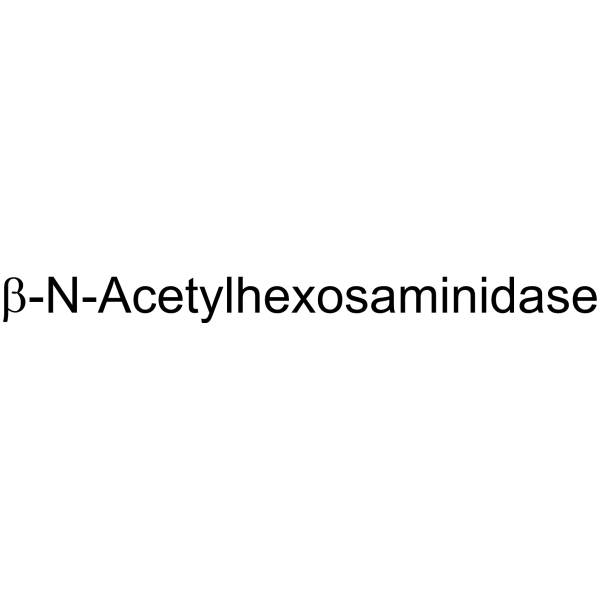 |
β-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶 来源于洋刀豆(刀豆)
CAS:9012-33-3 |
|
 |
精氨酸酶
CAS:9000-96-8 |