| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
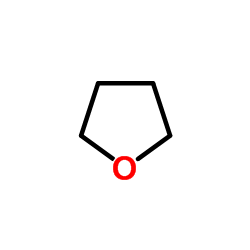 |
四氢呋喃
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
 |
蜂毒肽
CAS:20449-79-0 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
四氢呋喃
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
 |
蜂毒肽
CAS:20449-79-0 |