| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
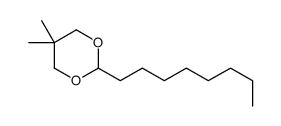 |
天然橡胶
CAS:9003-31-0 |
|
 |
香叶基焦磷酸铵盐
CAS:763-10-0 |
|
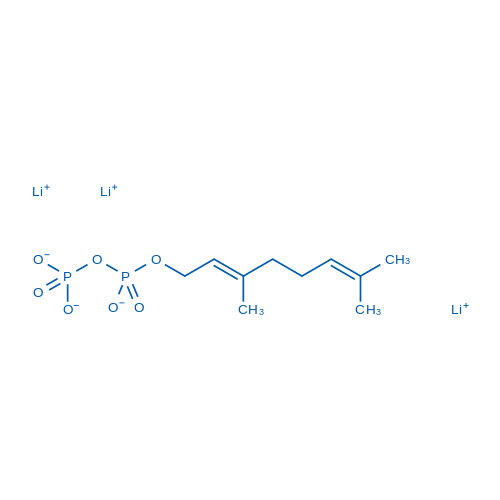 |
香叶基焦磷酸盐 锂盐
CAS:21141-43-5 |