| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
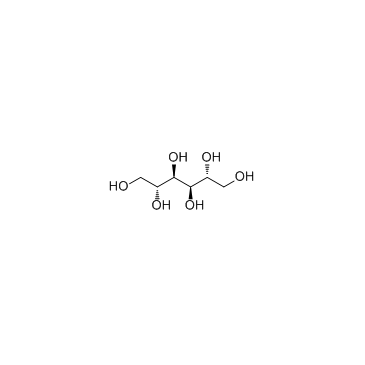 |
甘露醇
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
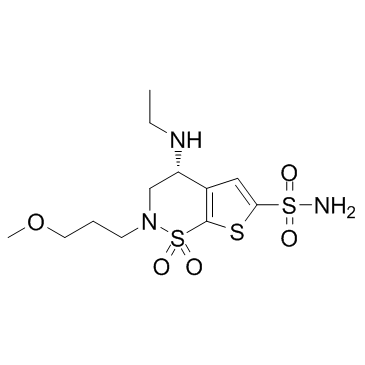 |
布林佐胺
CAS:138890-62-7 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘露醇
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
 |
布林佐胺
CAS:138890-62-7 |