Risk factors and outcome analysis of acinetobacter baumannii complex bacteremia in critical patients.
Hao-Yuan Lee, Chyi-Liang Chen, Si-Ru Wu, Chih-Wei Huang, Cheng-Hsun Chiu
文献索引:Crit. Care Med. 42(5) , 1081-8, (2014)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Acinetobacter baumannii complex bacteremia has been identified increasingly in critical patients admitted in ICUs. Notably, A. baumannii complex bacteremia has a high mortality rate, yet the risk factors associated with mortality remain unclear and controversial.Retrospective study.All adult ICUs at a tertiary care medical center.All patients with A. baumannii complex bacteremia admitted in 2009-2010.None.Risk factors for mortality were analyzed. Bacterial isolates were identified by 16S-23S ribosomal RNA intergenic spacer region sequencing for genospecies and genotyped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Carbapenemase genes were detected by polymerase chain reaction and sequencing. A total of 298 patients met the inclusion criteria, including 73 (24.5%) infected by imipenem-resistant A. baumannii complex. The overall 30-day mortality was 33.6% (100 of 298). Imipenem-resistant A. baumannii complex bacteremia specifically showed a high mortality (69.9%) and was associated with prior use of broad-spectrum antibiotics for more than 5 days for treating ventilator-associated pneumonia before the occurrence of bacteremia. Mortality was associated with inappropriate initial antimicrobial therapy, which was correlated with imipenem-resistant A. baumannii complex but not with any specific genospecies. ISAba1-blaOXA-23-ISAba1 (Tn2006) was found in most (66.7%, 40 of 68) imipenem-resistant A. baumannii (genospecies 2) and also spread beyond species border to all imipenem-resistant genospecies 3 (2), 13TU (2), and 10 (1).For critical patients with A. baumannii complex infection, ventilator-associated pneumonia in particular, the selective pressure from prior use of broad-spectrum antibiotics for 5 days or more increased risk of subsequent imipenem-resistant A. baumannii complex bacteremia. To reduce mortality, rapid identification of imipenem-resistant A. baumannii complex and early initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy in these high-risk patients are crucial.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
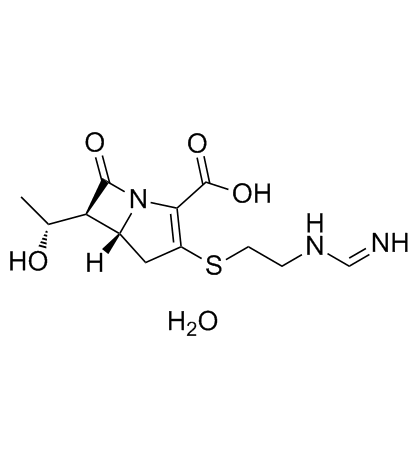 |
亚胺培南(一水物)
CAS:74431-23-5 |
C12H19N3O5S |
|
Combined disc methods for the detection of KPC- and/or VIM-p...
2013-09-01 [Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 19(9) , E412-5, (2013)] |
|
Inhibitory Potential of Twenty Five Anti-tuberculosis Drugs ...
2015-01-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 38 , 1425-9, (2015)] |
|
Colistin and doripenem combinations against Pseudomonas aeru...
2015-05-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 70 , 1434-42, (2015)] |
|
Identification of capsular types in carbapenem-resistant Kle...
2015-02-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 59(2) , 1038-47, (2015)] |
|
Activity of MK-7655 combined with imipenem against Enterobac...
2013-10-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 68(10) , 2286-90, (2013)] |