N-acetylneuraminic acid accumulation in a buoyant lysosomal fraction of cultured fibroblasts from patients with infantile generalized N-acetylneuraminic acid storage disease.
J Hildreth, L Sacks, L W Hancock
文献索引:Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 139(2) , 838-44, (1986)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Cultured fibroblasts from control individuals and two patients affected with the infantile variant of generalized N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc) storage disease were disrupted by nitrogen cavitation, and the post-nuclear supernatant fractions were subjected to subcellular fractionation on Percoll gradients. Accumulating NeuAc in affected fibroblasts (approx. 150 nmol/mg protein) co-localized with the lysosomal marker N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase (Hex), in a fraction with a mean density of 1.035 g/ml. In contrast, more than 70% of the Hex activity of control cells sedimented in comparable gradients with a density of more than 1.07 g/ml. The lysosomal localization of NeuAc accumulation in affected fibroblasts was confirmed by treatment of post-nuclear supernatant fractions with 0.5 mM Gly-Phe-beta-naphthylamide (20 min, 37 degrees C) prior to centrifugation, which resulted in the simultaneous loss of latency of Hex and free NeuAc, and their association with the soluble fraction on Percoll gradients. The results provide direct evidence for the accumulation of free NeuAc in a unique buoyant lysosomal fraction of affected fibroblasts.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
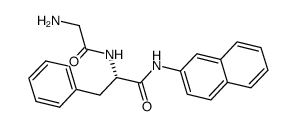 |
Gly-Phe-β-naphthylamide
CAS:21438-66-4 |
C21H21N3O2 |
|
Effect of glycyl-L-phenylalanine 2-naphthylamide on invertas...
1985-02-01 [Biochem. J. 225(3) , 645-8, (1985)] |
|
Constitutive lysosome exocytosis releases ATP and engages P2...
2012-10-01 [J. Cell Sci. 125(Pt 19) , 4567-75, (2012)] |
|
Calcium mobilization by nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide ...
2006-02-01 [Cell Calcium 39(2) , 143-53, (2006)] |
|
A confocal study on the visualization of chromaffin cell sec...
2010-12-01 [J. Struct. Biol. 172(3) , 261-9, (2010)] |
|
Expression and purification of active recombinant cathepsin ...
2009-01-01 [J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009 , 746289, (2009)] |