Structural insight into inositol pyrophosphate turnover.
Stephen B Shears, Jeremy D Weaver, Huanchen Wang
文献索引:Adv. Biol. Regul. 53(1) , 19-27, (2013)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The diphosphoinositol polyphosphates ("inositol pyrophosphates"; PP-InsPs) regulate many cellular processes in eukaryotes, including stress responses, apoptosis, vesicle trafficking, cytoskeletal dynamics, exocytosis, telomere maintenance, insulin signaling and neutrophil activation. Thus, the enzymes that control the metabolism of the PP-InsPs serve important cell signaling roles. In order to fully characterize how these enzymes are regulated, we need to determine the atomic-level architecture of their active sites. Only then can we fully appreciate reaction mechanisms and their modes of regulation. In this review, we summarize published information obtained from the structural analysis of a human diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase (DIPP), and a human diphosphoinositol polyphosphate kinase (PPIP5K). This work includes the analysis of crystal complexes with substrates, products, transition state analogs, and a novel phosphonoacetate substrate analog.Published by Elsevier Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
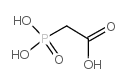 |
膦酰基乙酸
CAS:4408-78-0 |
C2H5O5P |
|
Equine Herpesvirus 1 Multiply Inserted Transmembrane Protein...
2015-06-15 [J. Virol. 89 , 6251-63, (2015)] |
|
Epstein-barr virus blocks the autophagic flux and appropriat...
2014-11-01 [J. Virol. 88(21) , 12715-26, (2014)] |
|
Viral semaphorin inhibits dendritic cell phagocytosis and mi...
2015-04-01 [J. Virol. 89(7) , 3630-47, (2015)] |
|
Interaction between the biotin carboxyl carrier domain and t...
2011-11-15 [Biochemistry 50(45) , 9708-23, (2011)] |
|
N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate induces TAp73-dependent apopt...
2013-02-14 [Oncogene 32(7) , 920-9, (2013)] |