Optimizing molluscicide treatment strategies in different control stages of schistosomiasis in the People's Republic of China.
Guo-Jing Yang, Le-Ping Sun, Qing-Biao Hong, Hong-Ru Zhu, Kun Yang, Qi Gao, Xiao-Nong Zhou
文献索引:Parasit. Vectors 5 , 260, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The application of chemical molluscicides is still one of the most effective measures for schistosomiasis control in P. R. China. By applying diverse molluscicide treatment scenarios on different snail densities in the field, we attempted to understand the cost-effectiveness of molluscicide application so as to prescribe an optimal management approach to control intermediate host snail Oncomelania hupensis under acceptable thresholds based on the goal of the National Schistosomiasis Control Programme.The molluscicidal field trial was carried out in the marshland of an island along the Yangtze River, Jiangsu province, P.R. China in October 2010. Three plots in the island representing low-density, medium-density and high-density groups were identified after the baseline survey on snail density. Each snail density plot was divided into four experimental units in which molluscicide (50% niclosamide ethanolamine salt wettable powder) was applied once, twice, trice and four times, respectively. The logistic regression model to correlate snail mortality rate with the covariates of number of molluscicidal treatment and snail density, and a linear regression model to investigate the relationship between cost-effectiveness and number of molluscicidal treatment as well as snail density were established.The study revealed that increase in the number of molluscicide treatments led to increased snail mortality across all three population density groups. The most cost-effective regimen was seen in the high snail density group with a single molluscicide treatment. For both high and low density groups, the more times molluscicide were applied, the less cost-effectiveness was. However, for the median density group, the level of cost-effectiveness for two applications was slightly higher than that in one time.We concluded that different stages of the national schistosomiasis control/elimination programme, namely morbidity control, transmission control and transmission interruption, should utilize different molluscicide treatment strategies to maximize cost-effectiveness.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
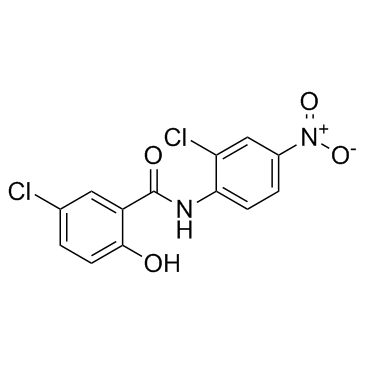 |
氯硝柳胺
CAS:50-65-7 |
C13H8Cl2N2O4 |
|
The salicylanilide derivatives inhibit signal transducer and...
2016-01-01 [Anticancer Drugs 27 , 41-7, (2015)] |
|
Taenia solium: Development of an Experimental Model of Porci...
2015-01-01 [PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 9 , e0003980, (2015)] |
|
Phase I and phase II reductive metabolism simulation of nitr...
2014-11-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(28) , 7253-60, (2014)] |
|
LGR5 is associated with tumor aggressiveness in papillary th...
2015-10-27 [Oncotarget 6 , 34549-60, (2015)] |
|
Validation of a streamlined multiclass, multiresidue method ...
2015-06-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 407 , 4423-35, (2015)] |