| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
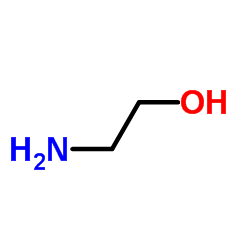 |
2-氨基乙醇
CAS:141-43-5 |
|
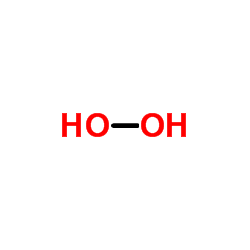 |
过氧化氢
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
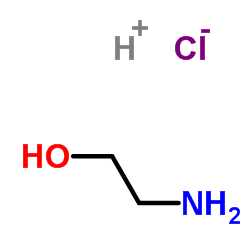 |
盐酸乙醇胺
CAS:2002-24-6 |
|
 |
雷帕霉素
CAS:53123-88-9 |
|
 |
桃叶珊瑚苷; 杜仲苷
CAS:479-98-1 |
|
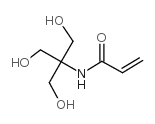 |
N-丙烯酰(三羟甲基)氨基甲烷
CAS:13880-05-2 |