Tamoxifen: evidence by 32P-postlabeling and use of metabolic inhibitors for two distinct pathways leading to mouse hepatic DNA adduct formation and identification of 4-hydroxytamoxifen as a proximate metabolite.
K Randerath, B Moorthy, N Mabon, P Sriram
文献索引:Carcinogenesis 15(10) , 2087-94, (1994)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Exposure to pentachlorophenol (PCP) strongly intensifies the formation of mouse hepatic DNA adducts elicited by oral administration of tamoxifen (TAM), as previously shown by 32P-postlabeling. To explain this effect, PCP was proposed to interfere with the detoxication by sulfate conjugation of an as yet unidentified hydroxylated proximate TAM metabolite. A comparison of the present and earlier results shows that the hepatic TAM adduct pattern in female ICR mice depended on the route of administration of TAM (120 mumol/kg), with oral administration primarily eliciting formation of more polar adducts (termed group I adducts), while after i.p. administration less polar adducts (group II) predominated over group I adducts by a factor of 17.5. All these adducts were also formed in female Sprague-Dawley rats after i.p. dosing with TAM, but total adduct levels were 3.5- to 5-fold higher than in mice. After four daily i.p. treatments, TAM adducts accumulated in mouse liver DNA in a non-linear fashion. Adduct levels were 30-50 times lower in mouse kidney and lung than in liver. The phenolic metabolite 4-hydroxy TAM (120 mumol/kg) exclusively led to formation of polar (group I) hepatic adducts, and this process was stimulated 8-fold by co-administration of PCP (75 mumol/kg). Co-administration of PCP with the parent compound led to an 11-fold enhancement of group I adduct formation; simultaneously, levels of group II adducts were suppressed 6-fold. Another inhibitor of sulfate conjugation, 2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenol, unlike PCP, had no effect on group I adducts, but it reduced group II adduct formation 2.2-fold. The PCP metabolite 2,3,5,6-tetrachlorohydroquinone (75 mumol/kg) did not significantly affect any major TAM adduct, suggesting that PCP itself was the active compound. Similar to group II TAM adducts, the formation of hepatic safrole-DNA adducts was inhibited in female ICR mice by both sulfotransferase inhibitors, consistent with the proposal that metabolic alpha-hydroxylation of the ethyl group of TAM followed by sulfate conjugation represented a mechanism of TAM activation. On the other hand, the strong intensification of group I adducts by PCP and the lack of this effect by 2,6-dichloro-4-nitrophenol suggested that inhibition of sulfate conjugation may not have been the primary mechanism underlying the intensification of group I adducts formed from TAM or 4-hydroxy TAM. The results presented herein demonstrate conclusively that TAM was activated to DNA-reactive compounds along two distinct pathways which contrasted in their responses to metabolic inhibitors.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
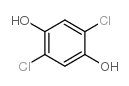 |
2,5-二氯对苯二酚
CAS:824-69-1 |
C6H4Cl2O2 |
|
Sequence analysis of a gene cluster involved in metabolism o...
1995-04-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61(4) , 1279-89, (1995)] |
|
Degradation of the chlorinated phenoxyacetate herbicides 2,4...
1990-05-01 [Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56(5) , 1357-62, (1990)] |
|
PcpA, which is involved in the degradation of pentachlorophe...
1999-10-15 [FEBS Lett. 459(3) , 395-8, (1999)] |
|
Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-...
1994-06-01 [J. Bacteriol. 176(11) , 3117-25, (1994)] |
|
Cloning and sequencing of a 2,5-dichlorohydroquinone reducti...
1998-03-01 [J. Bacteriol. 180(6) , 1354-9, (1998)] |