| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
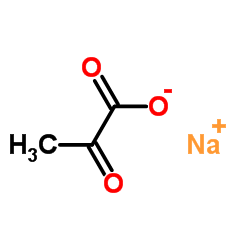 |
丙酮酸钠
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
HUMAN M-CSF
CAS:81627-83-0 |
|
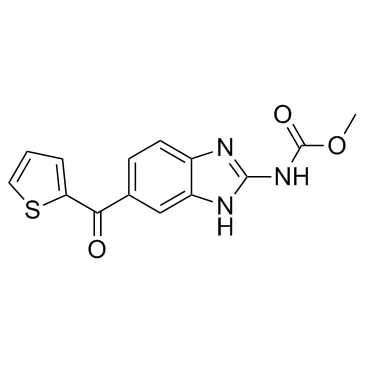 |
诺考达唑
CAS:31430-18-9 |