| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
酮康唑
CAS:65277-42-1 |
|
 |
甲醇
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
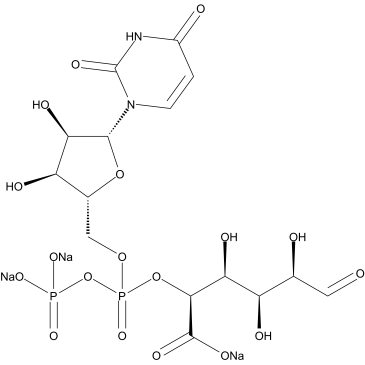 |
尿苷二磷酸葡糖醛酸
CAS:63700-19-6 |
|
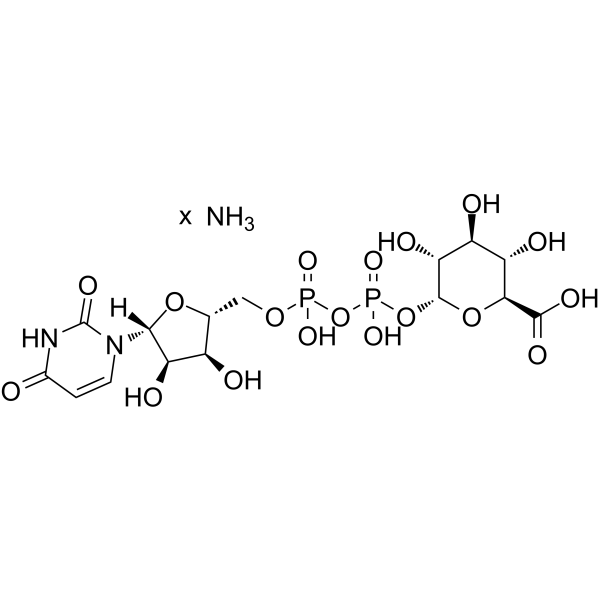 |
尿苷-5′-二磷酸葡糖醛酸 铵盐
CAS:43195-60-4 |
|
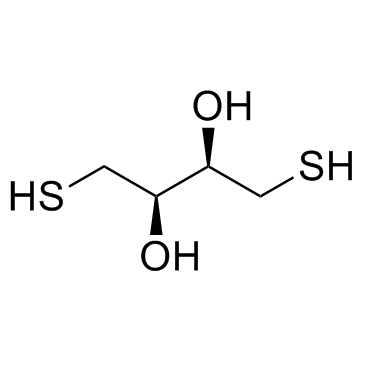 |
DL-二硫苏糖醇
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
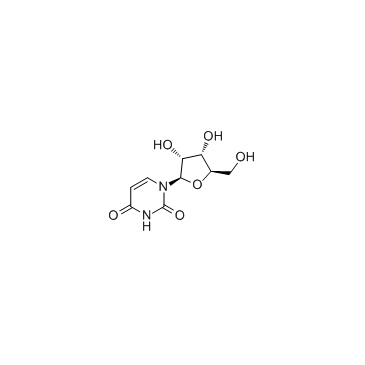 |
尿苷
CAS:58-96-8 |