| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
(±)-1-苯基-1,2-乙二醇
CAS:93-56-1 |
|
 |
(R)-(-)-1-苯基-1,2-乙二醇
CAS:16355-00-3 |
|
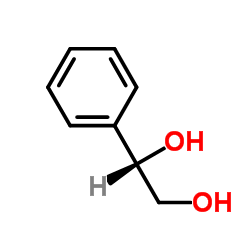 |
(S)-1-苯基-1,2-乙二醇
CAS:25779-13-9 |