| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
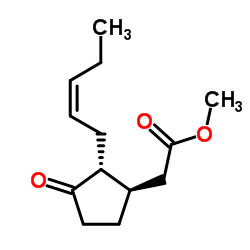 |
茉莉酸甲酯
CAS:39924-52-2 |
|
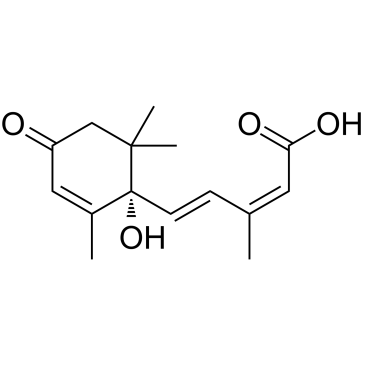 |
脱落酸
CAS:21293-29-8 |